Finding Feasible Solutions#
Constrained, gradient-based optimization tools like SLSQP, IPOPT, and SNOPT can benefit from starting from a feasible design point, but finding a feasible design with dozens or hundreds of design variables can be a challenge in itself.
Domain-specific methods exist for finding a feasible starting point, such as using a suboptimal explicit simulation to jump-start an implicit trajectory optimization, but in a multidisciplinary environment a more general approach is needed.
OpenMDAO’s Problem.find_feasible method aims to find a feasible point if one exists, or otherwise minimize the violation of infeasible constraints in the design.
This approach poses the constraint violations as residuals to be minimized via a least-squares approach. Under the hood, it utilizes scipy.optimize.least_squares to perform this minimization.
- Problem.find_feasible(case_prefix=None, reset_iter_counts=True, driver_scaling=True, exclude_desvars=None, method='trf', ftol=1e-08, xtol=1e-08, gtol=1e-08, x_scale=1.0, loss='linear', loss_tol=1e-08, f_scale=1.0, max_nfev=None, tr_solver=None, tr_options=None, iprint=1)[source]
Attempt to find design variable values which minimize the constraint violation.
If the problem is feasible, this method should find the solution for which the violation of each constraint is zero.
This approach uses a least-squares minimization of the constraint violation. If the problem has a feasible solution, this should find the feasible solution closest to the current design variable values.
Arguments method, ftol, xtol, gtol, x_scale, loss, f_scale, diff_step, tr_solver, tr_options, and verbose are passed to scipy.optimize.least_squares, see the documentation of that function for more information: https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.least_squares.html
- Parameters:
- case_prefixstr or None
Prefix to prepend to coordinates when recording. None means keep the preexisting prefix.
- reset_iter_countsbool
If True and model has been run previously, reset all iteration counters.
- driver_scalingbool
If True, consider the constraint violation in driver-scaled units. Otherwise, it will be computed in the model’s units.
- exclude_desvarsstr or Sequence[str] or None
If given, a pattern of one or more design variables to be excluded from the least-squares search. The allows for finding a feasible (or least infeasible) solution when holding one or more design variables to their current values.
- method{‘trf’, ‘dogbox’, or ‘lm’}
The method used by scipy.optimize.least_squares. One or ‘trf’, ‘dogbox’, or ‘lm’.
- ftolfloat or None
The change in the cost function from one iteration to the next which triggers a termination of the minimization.
- xtolfloat or None
The change in the design variable vector norm from one iteration to the next which triggers a termination of the minimization.
- gtolfloat or None
The change in the gradient norm from one iteration to the next which triggers a termination of the minimization.
- x_scale{float, array-like, or ‘jac’}
Additional scaling applied by the least-squares algorithm. Behavior is method-dependent. For additional details, see the scipy documentation.
- loss{‘linear’, ‘soft_l1’, ‘huber’, ‘cauchy’, or ‘arctan’}
The loss aggregation method. Options of interest are: - ‘linear’ gives the standard “sum-of-squares”. - ‘soft_l1’ gives a smooth approximation for the L1-norm of constraint violation. For other options, see the scipy documentation.
- loss_tolfloat
The tolerance on the loss value above which the algorithm is considered to have failed to find a feasible solution. This will result in the DriverResult.success attribute being False, and this method will return as _failed_.
- f_scalefloat or None
Value of margin between inlier and outlier residuals when loss is not ‘linear’. For more information, see the scipy documentation.
- max_nfevint or None
The maximum allowable number of model evaluations. If not provided scipy will determine it automatically based on the size of the design variable vector.
- tr_solver{None, ‘exact’, or ‘lsmr’}
The solver used by trust region (trf) method. For more details, see the scipy documentation.
- tr_optionsdict or None
Additional options for the trust region (trf) method. For more details, see the scipy documentation.
- iprintint
Verbosity of the output. Use 2 for the full verbose least_squares output. Use 1 for a convergence summary, and 0 to suppress output.
- Returns:
- bool
Failure flag; True if failed to converge, False is successful.
Consider the following optimization problem. It contains two constraints which are in conflict with each other.
The OpenMDAO problem can be formulated as follows:
import numpy as np
import openmdao.api as om
prob = om.Problem()
c1 = om.ExecComp()
c1.add_expr('y = x1**2 - x2**2', y={'copy_shape': 'x1'}, x1={'shape_by_conn': True}, x2={'shape_by_conn': True})
c1.add_expr('g1 = 2 * x1 - 5', g1={'copy_shape': 'x1'})
c1.add_expr('g2 = -2 * x1 - 5', g2={'copy_shape': 'x1'})
c1.add_expr('g3 = x2 - 5', g3={'copy_shape': 'x2'})
c1.add_design_var('x1', lower=-10, upper=10)
c1.add_design_var('x2', lower=-10, upper=10)
c1.add_objective('y')
c1.add_constraint('g1', lower=0)
c1.add_constraint('g2', lower=0)
c1.add_constraint('g3', lower=0)
prob.model.add_subsystem('c1', c1, promotes=['*'])
prob.driver = om.ScipyOptimizeDriver()
The feasible regions due to each constraint are shaded in the figure below. Note that there is no solution which satisfies all three constraints.
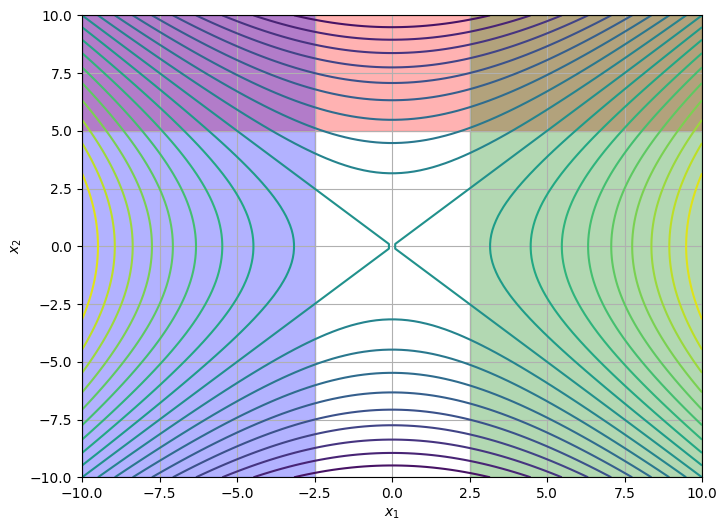
If we perform an optimization with the driver, it will fail due to the incompatible constraints.
# Call setup again so we can use a new size for x1 and x2
prob.setup()
prob.set_val('x1', 1.0)
prob.set_val('x2', 1.0)
prob.run_driver()
prob.list_driver_vars(cons_opts=['lower', 'upper'], objs_opts=['val']);
Positive directional derivative for linesearch (Exit mode 8)
Current function value: -98.99999999997303
Iterations: 10
Function evaluations: 26
Gradient evaluations: 6
Optimization FAILED.
Positive directional derivative for linesearch
-----------------------------------
----------------
Design Variables
----------------
name val size lower upper ref ref0 indices adder scaler parallel_deriv_color cache_linear_solution units
---- ----- ---- ----- ----- ---- ---- ------- ----- ------ -------------------- --------------------- -----
x1 [1.] 1 -10.0 10.0 None None None None None None False None
x2 [10.] 1 -10.0 10.0 None None None None None None False None
-----------
Constraints
-----------
name val size indices alias lower upper
---- ----- ---- ------- ----- ----- -----
g1 [-3.] 1 None None 0.0 1e+30
g2 [-7.] 1 None None 0.0 1e+30
g3 [5.] 1 None None 0.0 1e+30
----------
Objectives
----------
name val size indices
---- ------ ---- -------
y [-99.] 1 None
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/test/lib/python3.12/site-packages/openmdao/utils/coloring.py:447: DerivativesWarning:'c1' <class ExecComp>: Coloring was deactivated. Improvement of 0.0% was less than min allowed (5.0%).
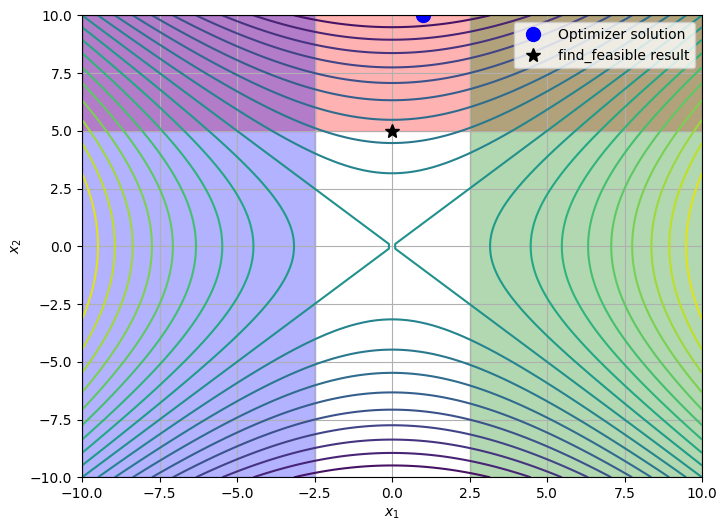
If we use the find_feasible method on Problem, we can find the solution which minimizes the L2 norm of the constraint violations.
This method will attempt to find the solution that minimizes the constraint violations. If it fails to converge to a solution, it will return as having failed.
If it converges but the solution is still infeasible (it found the solution which minimizes the constraint violation), it will also return as having failed.
x1_opt = prob.get_val('x1').copy()
x2_opt = prob.get_val('x2').copy()
prob.set_val('x1', 1.0)
prob.set_val('x2', 1.0)
prob.find_feasible()
prob.list_driver_vars(desvar_opts=['lower', 'upper'], cons_opts=['lower', 'upper'], objs_opts=['val']);
-------------------------
Infeasibilities minimized
-------------------------
loss(linear): 25.00000000
iterations: 7
model evals: 7
gradient evals: 7
elapsed time: 0.00302145 s
max violation: g1[0] = -5.00000000
----------------
Design Variables
----------------
name val size indices lower upper
---- ----------------- ---- ------- ----- -----
x1 [-2.93033752e-16] 1 None -10.0 10.0
x2 [5.] 1 None -10.0 10.0
-----------
Constraints
-----------
name val size indices alias lower upper
---- ----------------- ---- ------- ----- ----- -----
g1 [-5.] 1 None None 0.0 1e+30
g2 [-5.] 1 None None 0.0 1e+30
g3 [-3.99680289e-14] 1 None None 0.0 1e+30
----------
Objectives
----------
name val size indices
---- ------ ---- -------
y [-25.] 1 None
The following plot highlights the difference between the solution at the end of the failed optimization run, versus the solution found which minimizes feasibilities.
Omitting one or more design variables from the feasibility search#
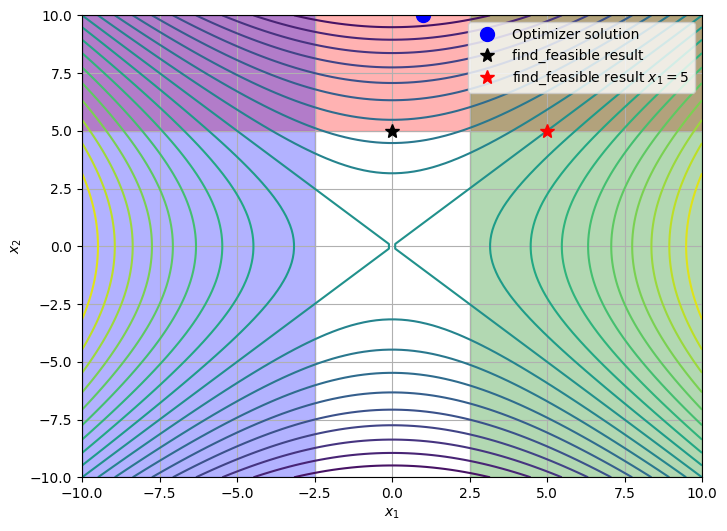
Sometimes the user may be interested in finding a feasible (or least infeasible) solution at a given value of one or more design variables.
The find_feasible method supports an exclude_desvars keyword argument that allows the user to exclude one or more design variables from the feasibility search. This argument may be a glob pattern which can match one or more design variable names.
For instance, let’s find the minimimum-infeasibility-solution such that \(x_1 = 5\).
prob.set_val('x1', 5.0)
prob.find_feasible(exclude_desvars=['x1'])
prob.list_driver_vars(desvar_opts=['lower', 'upper'], cons_opts=['lower', 'upper'], objs_opts=['val']);
-------------------------
Infeasibilities minimized
-------------------------
loss(linear): 112.50000000
iterations: 1
model evals: 1
gradient evals: 1
elapsed time: 0.00100186 s
max violation: g2[0] = -15.00000000
----------------
Design Variables
----------------
name val size indices lower upper
---- ---- ---- ------- ----- -----
x1 [5.] 1 None -10.0 10.0
x2 [5.] 1 None -10.0 10.0
-----------
Constraints
-----------
name val size indices alias lower upper
---- ----------------- ---- ------- ----- ----- -----
g1 [5.] 1 None None 0.0 1e+30
g2 [-15.] 1 None None 0.0 1e+30
g3 [-3.99680289e-14] 1 None None 0.0 1e+30
----------
Objectives
----------
name val size indices
---- ---------------- ---- -------
y [3.97903932e-13] 1 None
Starting an Optimization from a Feasible Point#
The find_feasible method iterates on the OpenMDAO model.
If it completes successfully, the model will be in a feasible state and optimization can begin immediately.
The following problem can be challenging to optimize from the default initial condition of [1, 1, 10, 1].
This problem is the cost minimization of a pressure vessel with the design variables being the thicknesses of the end-cap and cylindrical sections (d1 and d2), the vessel radius (r), and the length of the cylindrical section (L).
This example comes from Solving Engineering Optimization Problems with the Simple Constrained Particle Swarm Optimizer, by Cagnina et al., 2008.
Note that the original problem assumes integer values for d1 and d2 but they are continuous for the purpose of this demonstration.
p = om.Problem()
p.model.add_subsystem('vessel',
om.ExecComp(['f = 0.6224 * d1 * r * L + 1.7781 * d2 * r**2 + 3.1661 * d1**2 * L + 19.84 * d1**2 * r',
'g1 = -d1 + 0.0193 * r',
'g2 = -d2 + 0.00954 * r',
'g3 = -pi * r**2 * L - (4/3) * pi * r**3 + 1296000.'], has_diag_partials=True),
promotes=['*'])
p.model.add_design_var('d1', lower=0.0625)
p.model.add_design_var('d2', lower=0.0625, upper = 99 * 0.0625)
p.model.add_design_var('r', lower=10)
p.model.add_design_var('L', lower=1., upper=200.)
p.model.add_constraint('g1', upper=0)
p.model.add_constraint('g2', upper=0)
p.model.add_constraint('g3', upper=0, ref=1_000_000.)
p.model.add_objective('f', ref=1_000.)
p.driver = om.ScipyOptimizeDriver()
p.setup();
Instead, we’ll reset the design point to the initial naive value and use find_feasible to first try to find a solution that satisfies all constraints.
p.set_val('r', 10.) # Note we start r within its bounds for find_feasible.
p.run_model()
find_feas_fail = p.find_feasible()
--------------------
Feasible point found
--------------------
loss(linear): 0.00000000
iterations: 4
model evals: 4
gradient evals: 4
elapsed time: 0.00354516 s
max violation: N/A
The feasible starting point is:
p.list_driver_vars(desvar_opts=['lower', 'upper'], cons_opts=['lower', 'upper'], objs_opts=[]);
----------------
Design Variables
----------------
name val size indices lower upper
---- -------------- ---- ------- ------ ------
d1 [1.] 1 None 0.0625 1e+30
d2 [1.] 1 None 0.0625 6.1875
r [42.35232755] 1 None 10.0 1e+30
L [177.25886122] 1 None 1.0 200.0
-----------
Constraints
-----------
name val size indices alias lower upper
---- ------------- ---- ------- ----- ------ -----
g1 [-0.18260008] 1 None None -1e+30 0.0
g2 [-0.5959588] 1 None None -1e+30 0.0
g3 [-0.02109273] 1 None None -1e+30 0.0
----------
Objectives
----------
name val size indices
---- ------------ ---- -------
f [9.26346166] 1 None
Now the problem is in a state such that the problem is feasible, run the driver.
opt_fail = p.run_driver()
p.list_driver_vars(desvar_opts=['lower', 'upper'], cons_opts=['lower', 'upper'], objs_opts=[]);
Optimization terminated successfully (Exit mode 0)
Current function value: 5.885332773625331
Iterations: 11
Function evaluations: 11
Gradient evaluations: 11
Optimization Complete
-----------------------------------
----------------
Design Variables
----------------
name val size indices lower upper
---- ------------- ---- ------- ------ ------
d1 [0.77816864] 1 None 0.0625 1e+30
d2 [0.38464916] 1 None 0.0625 6.1875
r [40.31961872] 1 None 10.0 1e+30
L [200.] 1 None 1.0 200.0
-----------
Constraints
-----------
name val size indices alias lower upper
---- ----------------- ---- ------- ----- ------ -----
g1 [-3.91908728e-14] 1 None None -1e+30 0.0
g2 [-8.31001934e-14] 1 None None -1e+30 0.0
g3 [-1.79000199e-12] 1 None None -1e+30 0.0
----------
Objectives
----------
name val size indices
---- ------------ ---- -------
f [5.88533277] 1 None
